Back
SPVs
SPV Syndicate Fundraising: How Syndicates Use Special Purpose Vehicles to Raise Capital Efficiently
SPV Syndicate Fundraising: How Syndicates Use Special Purpose Vehicles to Raise Capital Efficiently
SPV Syndicate Fundraising: How Syndicates Use Special Purpose Vehicles to Raise Capital Efficiently
SPV syndicate fundraising has become one of the most important mechanisms in modern private markets, particularly in venture capital, private equity co-investments, and real estate deals. As deal access becomes more competitive and investors seek greater transparency and control, syndicates backed by Special Purpose Vehicles (SPVs) are reshaping how capital is raised and deployed.
At its core, SPV syndicate fundraising combines two powerful ideas: syndication, where a lead investor brings together multiple participants around a single deal, and SPV structuring, which provides the legal and financial framework to pool that capital efficiently. This hybrid model allows investors to participate in high-quality private opportunities without the complexity of direct ownership or the rigidity of traditional funds.
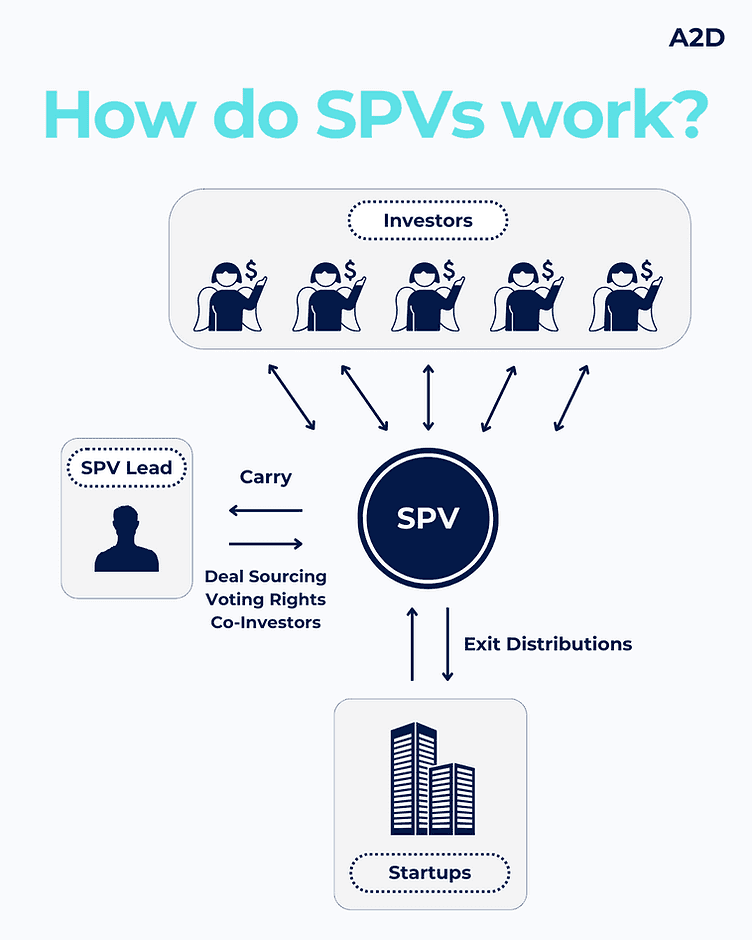
What Is SPV Syndicate Fundraising?
SPV syndicate fundraising refers to the process by which a lead investor (or syndicate lead) raises capital from multiple investors into a single SPV to execute one specific investment. The SPV acts as the legal wrapper that consolidates all syndicate participants into a single investing entity.
Rather than each investor negotiating directly with the target company or asset owner, the SPV appears as a single investor on the cap table or ownership register. Economically, each participant owns a proportional interest in the SPV, which in turn owns the underlying investment.
This structure allows syndicates to scale efficiently, enabling dozens—or even hundreds—of investors to participate in a deal without creating administrative or governance complexity for the underlying company.
Why SPV Syndicate Fundraising Is Growing Rapidly
The rise of SPV syndicate fundraising is driven by structural shifts in private markets.
First, access to high-quality private deals is increasingly relationship-driven. Syndicates led by experienced operators, angels, or fund managers often secure allocations that are unavailable to individual investors. The SPV enables these leads to aggregate capital quickly and professionally.
Second, investors want deal-by-deal choice. Rather than committing capital to a blind-pool fund, syndicate participants can selectively invest in opportunities that align with their risk tolerance, sector focus, and portfolio strategy.
Third, founders and asset owners prefer simplicity. An SPV-backed syndicate presents itself as a single investor, avoiding fragmented ownership and reducing long-term governance friction.
How SPV Syndicate Fundraising Works Step by Step
The SPV syndicate fundraising process typically begins with the syndicate lead sourcing a specific investment opportunity. This may be a startup funding round, a private equity co-investment, or a real estate transaction.
Once the lead secures preliminary terms, an SPV is formed specifically for that deal. The SPV’s legal documents define investor rights, economics, governance, and distribution mechanics.
The lead then opens the syndicate to investors. Participants review deal materials and commit capital through subscription agreements. Capital commitments are aggregated into the SPV until the target raise amount is reached.
After fundraising closes, the SPV executes the investment. From that point forward, all cash flows—whether dividends, interest, or exit proceeds—flow back into the SPV before being distributed to syndicate participants.
This process allows syndicates to raise capital quickly while maintaining institutional-grade structure.
Role of the Syndicate Lead
The syndicate lead plays a central role in SPV syndicate fundraising.
Unlike a traditional fund manager, the lead is typically focused on deal sourcing, diligence, and relationship management rather than ongoing portfolio construction. Their reputation, track record, and access are often the primary reasons investors participate in the syndicate.
In return, the lead may receive carried interest, a deal fee, or other performance-based compensation. This aligns incentives while avoiding the fixed management fees common in funds.
Because governance in SPVs is intentionally lightweight, trust in the syndicate lead is critical. Clear disclosure, alignment of incentives, and transparent communication are essential to maintaining credibility.
SPV Syndicate Fundraising vs Traditional Syndicates
Before SPVs became common, syndicates often relied on informal arrangements or direct investment structures. These approaches created significant challenges, including fragmented ownership, inconsistent documentation, and operational risk.
SPV syndicate fundraising professionalizes the syndicate model. The SPV standardizes investor onboarding, reporting, and distributions, while providing legal isolation and regulatory clarity.
This evolution has enabled syndicates to scale beyond small angel groups into institutional-quality investment vehicles capable of participating in large, competitive rounds.
SPV Syndicate Fundraising vs Fund Structures
Comparing SPV syndicate fundraising to traditional fund structures highlights important differences.
Funds raise capital upfront and deploy it across multiple investments at the manager’s discretion. Syndicate SPVs raise capital only after a specific deal is identified. This gives investors greater control and visibility but reduces diversification within each vehicle.
SPV syndicates are therefore best suited for high-conviction, opportunistic investments, while funds remain optimal for diversified, long-term strategies.
In practice, many investors use SPV syndicates as a complement to fund exposure rather than a replacement.
Investor Experience in SPV Syndicate Fundraising
From the investor’s perspective, SPV syndicate fundraising offers a more transparent and flexible experience.
Investors review a concrete opportunity with defined valuation, ownership structure, and exit scenarios. Reporting is straightforward, as performance is tied to a single asset.
However, this clarity comes with trade-offs. SPV syndicates concentrate risk in one deal, and liquidity is typically limited until an exit occurs. Investors must be comfortable with both the investment risk and the lead’s execution capability.
As a result, SPV syndicate fundraising is most attractive to investors who already have diversified portfolios and are seeking targeted exposure.
Economics and Fees in SPV Syndicate Fundraising
Fee structures in SPV syndicate fundraising are typically lighter than those of traditional funds.
Most syndicate SPVs do not charge annual management fees. Instead, economics often include a carried interest for the syndicate lead and reimbursement of administrative expenses. This aligns compensation with performance rather than capital raised.
Because syndicates are deal-specific, economics can vary widely depending on deal quality, lead reputation, and investor demand.
For investors, this often results in lower overall fees compared to fund investing, particularly for high-conviction opportunities.
Legal, Regulatory, and Compliance Considerations
SPV syndicate fundraising generally operates under private placement exemptions, limiting participation to accredited or professional investors. This framework balances capital formation efficiency with investor protection.
Jurisdictional choices affect tax treatment, reporting requirements, and cross-border participation. Proper structuring is essential to avoid regulatory risk that could undermine the syndicate’s effectiveness.
Well-run syndicates prioritize compliance, documentation, and transparency, recognizing that trust and professionalism are critical to long-term success.
Operational Complexity and the Role of Technology
Historically, running syndicates at scale was operationally difficult. Each SPV required bespoke legal work, accounting, and investor management.
Today, modern SPV platforms and fund administration tools are transforming SPV syndicate fundraising into a repeatable process. Automated onboarding, standardized documentation, and digital reporting reduce friction for both leads and investors.
This infrastructure shift is a major reason SPV syndicate fundraising has expanded rapidly across private markets.
SPV Syndicate Fundraising Across Asset Classes
SPV syndicate fundraising is most visible in venture capital, where angel syndicates aggregate capital into later-stage rounds. However, its use is expanding.
In private equity, syndicate SPVs enable co-investments alongside lead sponsors. In real estate, syndicate SPVs pool capital for single-asset acquisitions. In private credit, syndicates form SPVs to fund loan portfolios or structured deals.
This versatility underscores the adaptability of the SPV syndicate model.
Strategic Importance of SPV Syndicate Fundraising
SPV syndicate fundraising sits at the intersection of access, flexibility, and efficiency.
For syndicate leads, it enables scalable capital formation without the overhead of running a full fund. For investors, it provides curated access to deals with transparency and control. For founders and asset owners, it simplifies ownership and governance.
As private markets continue to grow, SPV syndicate fundraising is becoming a core pillar of modern capital formation.
Final Thoughts
SPV syndicate fundraising represents the professionalization of syndication. By combining trusted deal leads with institutional-grade SPV structures, it creates a powerful model for deal-based investing.
For investors and sponsors alike, understanding how SPV syndicate fundraising works—and when to use it—is essential for navigating today’s private markets. As flexibility and access become competitive advantages, SPV-backed syndicates are no longer fringe tools; they are foundational infrastructure.
SPV syndicate fundraising has become one of the most important mechanisms in modern private markets, particularly in venture capital, private equity co-investments, and real estate deals. As deal access becomes more competitive and investors seek greater transparency and control, syndicates backed by Special Purpose Vehicles (SPVs) are reshaping how capital is raised and deployed.
At its core, SPV syndicate fundraising combines two powerful ideas: syndication, where a lead investor brings together multiple participants around a single deal, and SPV structuring, which provides the legal and financial framework to pool that capital efficiently. This hybrid model allows investors to participate in high-quality private opportunities without the complexity of direct ownership or the rigidity of traditional funds.

What Is SPV Syndicate Fundraising?
SPV syndicate fundraising refers to the process by which a lead investor (or syndicate lead) raises capital from multiple investors into a single SPV to execute one specific investment. The SPV acts as the legal wrapper that consolidates all syndicate participants into a single investing entity.
Rather than each investor negotiating directly with the target company or asset owner, the SPV appears as a single investor on the cap table or ownership register. Economically, each participant owns a proportional interest in the SPV, which in turn owns the underlying investment.
This structure allows syndicates to scale efficiently, enabling dozens—or even hundreds—of investors to participate in a deal without creating administrative or governance complexity for the underlying company.
Why SPV Syndicate Fundraising Is Growing Rapidly
The rise of SPV syndicate fundraising is driven by structural shifts in private markets.
First, access to high-quality private deals is increasingly relationship-driven. Syndicates led by experienced operators, angels, or fund managers often secure allocations that are unavailable to individual investors. The SPV enables these leads to aggregate capital quickly and professionally.
Second, investors want deal-by-deal choice. Rather than committing capital to a blind-pool fund, syndicate participants can selectively invest in opportunities that align with their risk tolerance, sector focus, and portfolio strategy.
Third, founders and asset owners prefer simplicity. An SPV-backed syndicate presents itself as a single investor, avoiding fragmented ownership and reducing long-term governance friction.
How SPV Syndicate Fundraising Works Step by Step
The SPV syndicate fundraising process typically begins with the syndicate lead sourcing a specific investment opportunity. This may be a startup funding round, a private equity co-investment, or a real estate transaction.
Once the lead secures preliminary terms, an SPV is formed specifically for that deal. The SPV’s legal documents define investor rights, economics, governance, and distribution mechanics.
The lead then opens the syndicate to investors. Participants review deal materials and commit capital through subscription agreements. Capital commitments are aggregated into the SPV until the target raise amount is reached.
After fundraising closes, the SPV executes the investment. From that point forward, all cash flows—whether dividends, interest, or exit proceeds—flow back into the SPV before being distributed to syndicate participants.
This process allows syndicates to raise capital quickly while maintaining institutional-grade structure.
Role of the Syndicate Lead
The syndicate lead plays a central role in SPV syndicate fundraising.
Unlike a traditional fund manager, the lead is typically focused on deal sourcing, diligence, and relationship management rather than ongoing portfolio construction. Their reputation, track record, and access are often the primary reasons investors participate in the syndicate.
In return, the lead may receive carried interest, a deal fee, or other performance-based compensation. This aligns incentives while avoiding the fixed management fees common in funds.
Because governance in SPVs is intentionally lightweight, trust in the syndicate lead is critical. Clear disclosure, alignment of incentives, and transparent communication are essential to maintaining credibility.
SPV Syndicate Fundraising vs Traditional Syndicates
Before SPVs became common, syndicates often relied on informal arrangements or direct investment structures. These approaches created significant challenges, including fragmented ownership, inconsistent documentation, and operational risk.
SPV syndicate fundraising professionalizes the syndicate model. The SPV standardizes investor onboarding, reporting, and distributions, while providing legal isolation and regulatory clarity.
This evolution has enabled syndicates to scale beyond small angel groups into institutional-quality investment vehicles capable of participating in large, competitive rounds.
SPV Syndicate Fundraising vs Fund Structures
Comparing SPV syndicate fundraising to traditional fund structures highlights important differences.
Funds raise capital upfront and deploy it across multiple investments at the manager’s discretion. Syndicate SPVs raise capital only after a specific deal is identified. This gives investors greater control and visibility but reduces diversification within each vehicle.
SPV syndicates are therefore best suited for high-conviction, opportunistic investments, while funds remain optimal for diversified, long-term strategies.
In practice, many investors use SPV syndicates as a complement to fund exposure rather than a replacement.
Investor Experience in SPV Syndicate Fundraising
From the investor’s perspective, SPV syndicate fundraising offers a more transparent and flexible experience.
Investors review a concrete opportunity with defined valuation, ownership structure, and exit scenarios. Reporting is straightforward, as performance is tied to a single asset.
However, this clarity comes with trade-offs. SPV syndicates concentrate risk in one deal, and liquidity is typically limited until an exit occurs. Investors must be comfortable with both the investment risk and the lead’s execution capability.
As a result, SPV syndicate fundraising is most attractive to investors who already have diversified portfolios and are seeking targeted exposure.
Economics and Fees in SPV Syndicate Fundraising
Fee structures in SPV syndicate fundraising are typically lighter than those of traditional funds.
Most syndicate SPVs do not charge annual management fees. Instead, economics often include a carried interest for the syndicate lead and reimbursement of administrative expenses. This aligns compensation with performance rather than capital raised.
Because syndicates are deal-specific, economics can vary widely depending on deal quality, lead reputation, and investor demand.
For investors, this often results in lower overall fees compared to fund investing, particularly for high-conviction opportunities.
Legal, Regulatory, and Compliance Considerations
SPV syndicate fundraising generally operates under private placement exemptions, limiting participation to accredited or professional investors. This framework balances capital formation efficiency with investor protection.
Jurisdictional choices affect tax treatment, reporting requirements, and cross-border participation. Proper structuring is essential to avoid regulatory risk that could undermine the syndicate’s effectiveness.
Well-run syndicates prioritize compliance, documentation, and transparency, recognizing that trust and professionalism are critical to long-term success.
Operational Complexity and the Role of Technology
Historically, running syndicates at scale was operationally difficult. Each SPV required bespoke legal work, accounting, and investor management.
Today, modern SPV platforms and fund administration tools are transforming SPV syndicate fundraising into a repeatable process. Automated onboarding, standardized documentation, and digital reporting reduce friction for both leads and investors.
This infrastructure shift is a major reason SPV syndicate fundraising has expanded rapidly across private markets.
SPV Syndicate Fundraising Across Asset Classes
SPV syndicate fundraising is most visible in venture capital, where angel syndicates aggregate capital into later-stage rounds. However, its use is expanding.
In private equity, syndicate SPVs enable co-investments alongside lead sponsors. In real estate, syndicate SPVs pool capital for single-asset acquisitions. In private credit, syndicates form SPVs to fund loan portfolios or structured deals.
This versatility underscores the adaptability of the SPV syndicate model.
Strategic Importance of SPV Syndicate Fundraising
SPV syndicate fundraising sits at the intersection of access, flexibility, and efficiency.
For syndicate leads, it enables scalable capital formation without the overhead of running a full fund. For investors, it provides curated access to deals with transparency and control. For founders and asset owners, it simplifies ownership and governance.
As private markets continue to grow, SPV syndicate fundraising is becoming a core pillar of modern capital formation.
Final Thoughts
SPV syndicate fundraising represents the professionalization of syndication. By combining trusted deal leads with institutional-grade SPV structures, it creates a powerful model for deal-based investing.
For investors and sponsors alike, understanding how SPV syndicate fundraising works—and when to use it—is essential for navigating today’s private markets. As flexibility and access become competitive advantages, SPV-backed syndicates are no longer fringe tools; they are foundational infrastructure.
SPV syndicate fundraising has become one of the most important mechanisms in modern private markets, particularly in venture capital, private equity co-investments, and real estate deals. As deal access becomes more competitive and investors seek greater transparency and control, syndicates backed by Special Purpose Vehicles (SPVs) are reshaping how capital is raised and deployed.
At its core, SPV syndicate fundraising combines two powerful ideas: syndication, where a lead investor brings together multiple participants around a single deal, and SPV structuring, which provides the legal and financial framework to pool that capital efficiently. This hybrid model allows investors to participate in high-quality private opportunities without the complexity of direct ownership or the rigidity of traditional funds.

What Is SPV Syndicate Fundraising?
SPV syndicate fundraising refers to the process by which a lead investor (or syndicate lead) raises capital from multiple investors into a single SPV to execute one specific investment. The SPV acts as the legal wrapper that consolidates all syndicate participants into a single investing entity.
Rather than each investor negotiating directly with the target company or asset owner, the SPV appears as a single investor on the cap table or ownership register. Economically, each participant owns a proportional interest in the SPV, which in turn owns the underlying investment.
This structure allows syndicates to scale efficiently, enabling dozens—or even hundreds—of investors to participate in a deal without creating administrative or governance complexity for the underlying company.
Why SPV Syndicate Fundraising Is Growing Rapidly
The rise of SPV syndicate fundraising is driven by structural shifts in private markets.
First, access to high-quality private deals is increasingly relationship-driven. Syndicates led by experienced operators, angels, or fund managers often secure allocations that are unavailable to individual investors. The SPV enables these leads to aggregate capital quickly and professionally.
Second, investors want deal-by-deal choice. Rather than committing capital to a blind-pool fund, syndicate participants can selectively invest in opportunities that align with their risk tolerance, sector focus, and portfolio strategy.
Third, founders and asset owners prefer simplicity. An SPV-backed syndicate presents itself as a single investor, avoiding fragmented ownership and reducing long-term governance friction.
How SPV Syndicate Fundraising Works Step by Step
The SPV syndicate fundraising process typically begins with the syndicate lead sourcing a specific investment opportunity. This may be a startup funding round, a private equity co-investment, or a real estate transaction.
Once the lead secures preliminary terms, an SPV is formed specifically for that deal. The SPV’s legal documents define investor rights, economics, governance, and distribution mechanics.
The lead then opens the syndicate to investors. Participants review deal materials and commit capital through subscription agreements. Capital commitments are aggregated into the SPV until the target raise amount is reached.
After fundraising closes, the SPV executes the investment. From that point forward, all cash flows—whether dividends, interest, or exit proceeds—flow back into the SPV before being distributed to syndicate participants.
This process allows syndicates to raise capital quickly while maintaining institutional-grade structure.
Role of the Syndicate Lead
The syndicate lead plays a central role in SPV syndicate fundraising.
Unlike a traditional fund manager, the lead is typically focused on deal sourcing, diligence, and relationship management rather than ongoing portfolio construction. Their reputation, track record, and access are often the primary reasons investors participate in the syndicate.
In return, the lead may receive carried interest, a deal fee, or other performance-based compensation. This aligns incentives while avoiding the fixed management fees common in funds.
Because governance in SPVs is intentionally lightweight, trust in the syndicate lead is critical. Clear disclosure, alignment of incentives, and transparent communication are essential to maintaining credibility.
SPV Syndicate Fundraising vs Traditional Syndicates
Before SPVs became common, syndicates often relied on informal arrangements or direct investment structures. These approaches created significant challenges, including fragmented ownership, inconsistent documentation, and operational risk.
SPV syndicate fundraising professionalizes the syndicate model. The SPV standardizes investor onboarding, reporting, and distributions, while providing legal isolation and regulatory clarity.
This evolution has enabled syndicates to scale beyond small angel groups into institutional-quality investment vehicles capable of participating in large, competitive rounds.
SPV Syndicate Fundraising vs Fund Structures
Comparing SPV syndicate fundraising to traditional fund structures highlights important differences.
Funds raise capital upfront and deploy it across multiple investments at the manager’s discretion. Syndicate SPVs raise capital only after a specific deal is identified. This gives investors greater control and visibility but reduces diversification within each vehicle.
SPV syndicates are therefore best suited for high-conviction, opportunistic investments, while funds remain optimal for diversified, long-term strategies.
In practice, many investors use SPV syndicates as a complement to fund exposure rather than a replacement.
Investor Experience in SPV Syndicate Fundraising
From the investor’s perspective, SPV syndicate fundraising offers a more transparent and flexible experience.
Investors review a concrete opportunity with defined valuation, ownership structure, and exit scenarios. Reporting is straightforward, as performance is tied to a single asset.
However, this clarity comes with trade-offs. SPV syndicates concentrate risk in one deal, and liquidity is typically limited until an exit occurs. Investors must be comfortable with both the investment risk and the lead’s execution capability.
As a result, SPV syndicate fundraising is most attractive to investors who already have diversified portfolios and are seeking targeted exposure.
Economics and Fees in SPV Syndicate Fundraising
Fee structures in SPV syndicate fundraising are typically lighter than those of traditional funds.
Most syndicate SPVs do not charge annual management fees. Instead, economics often include a carried interest for the syndicate lead and reimbursement of administrative expenses. This aligns compensation with performance rather than capital raised.
Because syndicates are deal-specific, economics can vary widely depending on deal quality, lead reputation, and investor demand.
For investors, this often results in lower overall fees compared to fund investing, particularly for high-conviction opportunities.
Legal, Regulatory, and Compliance Considerations
SPV syndicate fundraising generally operates under private placement exemptions, limiting participation to accredited or professional investors. This framework balances capital formation efficiency with investor protection.
Jurisdictional choices affect tax treatment, reporting requirements, and cross-border participation. Proper structuring is essential to avoid regulatory risk that could undermine the syndicate’s effectiveness.
Well-run syndicates prioritize compliance, documentation, and transparency, recognizing that trust and professionalism are critical to long-term success.
Operational Complexity and the Role of Technology
Historically, running syndicates at scale was operationally difficult. Each SPV required bespoke legal work, accounting, and investor management.
Today, modern SPV platforms and fund administration tools are transforming SPV syndicate fundraising into a repeatable process. Automated onboarding, standardized documentation, and digital reporting reduce friction for both leads and investors.
This infrastructure shift is a major reason SPV syndicate fundraising has expanded rapidly across private markets.
SPV Syndicate Fundraising Across Asset Classes
SPV syndicate fundraising is most visible in venture capital, where angel syndicates aggregate capital into later-stage rounds. However, its use is expanding.
In private equity, syndicate SPVs enable co-investments alongside lead sponsors. In real estate, syndicate SPVs pool capital for single-asset acquisitions. In private credit, syndicates form SPVs to fund loan portfolios or structured deals.
This versatility underscores the adaptability of the SPV syndicate model.
Strategic Importance of SPV Syndicate Fundraising
SPV syndicate fundraising sits at the intersection of access, flexibility, and efficiency.
For syndicate leads, it enables scalable capital formation without the overhead of running a full fund. For investors, it provides curated access to deals with transparency and control. For founders and asset owners, it simplifies ownership and governance.
As private markets continue to grow, SPV syndicate fundraising is becoming a core pillar of modern capital formation.
Final Thoughts
SPV syndicate fundraising represents the professionalization of syndication. By combining trusted deal leads with institutional-grade SPV structures, it creates a powerful model for deal-based investing.
For investors and sponsors alike, understanding how SPV syndicate fundraising works—and when to use it—is essential for navigating today’s private markets. As flexibility and access become competitive advantages, SPV-backed syndicates are no longer fringe tools; they are foundational infrastructure.
Take the next step with Allocations
Take the next step with Allocations
Take the next step with Allocations
SPVs
Top Upcoming IPOs in 2026 : Allocations Research
Top Upcoming IPOs in 2026 : Allocations Research
Read more
SPVs
Why Digital Asset Treasury Companies (DATCOs) Will Lead 2026
Why Digital Asset Treasury Companies (DATCOs) Will Lead 2026
Read more
Company
Revolutionizing Fund Management: The Evolution of Allocations.com in 2025
Revolutionizing Fund Management: The Evolution of Allocations.com in 2025
Read more
SPVs
How do you structure an SPV into another SPV?
How do you structure an SPV into another SPV?
Read more
SPVs
What are secondary SPVs?
What are secondary SPVs?
Read more
Fund Manager
Watch out school VC: the podcasters are coming
Watch out school VC: the podcasters are coming
Read more
Fund Manager
Fast, hassle-free SPVs mean more time for due diligence
Fast, hassle-free SPVs mean more time for due diligence
Read more
Analytics
The rise of opportunity funds and why fund managers might need to start using them
The rise of opportunity funds and why fund managers might need to start using them
Read more
Analytics
Move as fast as founders do with instant SPVs
Move as fast as founders do with instant SPVs
Read more
Fund Manager
4 practical things LPs and fund managers need to know for tax season
4 practical things LPs and fund managers need to know for tax season
Read more
Fund Manager
Keep up with these 4 VC firms focused on crypto and blockchain
Keep up with these 4 VC firms focused on crypto and blockchain
Read more
Fund Manager
Fill your moleskine journals with tips from these 5 timeless angel investing blogs
Fill your moleskine journals with tips from these 5 timeless angel investing blogs
Read more
Company
Allocations partners with angeles investors to support hispanic and latinx founders and investors
Allocations partners with angeles investors to support hispanic and latinx founders and investors
Read more
SPVs
SPV in Venture Capital: How SPVs Are Used to Invest in Startups
SPV in Venture Capital: How SPVs Are Used to Invest in Startups
Read more
SPVs
Why Allocations Is the Best Fund Admin?
Why Allocations Is the Best Fund Admin?
Read more
SPVs
SPV Syndicate Fundraising: How Syndicates Use Special Purpose Vehicles to Raise Capital Efficiently
SPV Syndicate Fundraising: How Syndicates Use Special Purpose Vehicles to Raise Capital Efficiently
Read more
SPVs
SPV Fundraising: How Special Purpose Vehicles Are Transforming Deal-Based Capital Formation
SPV Fundraising: How Special Purpose Vehicles Are Transforming Deal-Based Capital Formation
Read more
SPVs
SPV Capital Raising: How SPVs Enable Efficient Deal-Based Funding
SPV Capital Raising: How SPVs Enable Efficient Deal-Based Funding
Read more
SPVs
SPV vs Fund Structure: Choosing the Right Investment Vehicle in Private Markets
SPV vs Fund Structure: Choosing the Right Investment Vehicle in Private Markets
Read more
SPVs
SPV Investment Structure: How Special Purpose Vehicles Are Designed for Modern Investing
SPV Investment Structure: How Special Purpose Vehicles Are Designed for Modern Investing
Read more
SPVs
SPV Financing: A Complete Guide to Structure, Use Cases, and Investment Strategy
SPV Financing: A Complete Guide to Structure, Use Cases, and Investment Strategy
Read more
SPVs
Real Estate SPVs: A Modern Framework for Structured Property Investing
Real Estate SPVs: A Modern Framework for Structured Property Investing
Read more
SPVs
ADGM Private Company Limited by Shares: Allocations Research
ADGM Private Company Limited by Shares: Allocations Research
Read more
SPVs
Offshore Company vs Onshore Company: Key Differences Explained
Offshore Company vs Onshore Company: Key Differences Explained
Read more
SPVs
What Is Offshore? Meaning, Uses, and How Offshore Structures Work in 2026
What Is Offshore? Meaning, Uses, and How Offshore Structures Work in 2026
Read more
SPVs
The Best Fund Admins for Emerging VCs (2026)
The Best Fund Admins for Emerging VCs (2026)
Read more
SPVs
How to Choose the Right Jurisdiction for an Offshore Company
How to Choose the Right Jurisdiction for an Offshore Company
Read more
SPVs
How to Start an Offshore Company: Allocations Guide 2026
How to Start an Offshore Company: Allocations Guide 2026
Read more
SPVs
Types of Special Purpose Vehicles (SPVs) and How Allocations Powers Them
Types of Special Purpose Vehicles (SPVs) and How Allocations Powers Them
Read more
SPVs
SPV vs Fund: Choose better with Allocation
SPV vs Fund: Choose better with Allocation
Read more
SPVs
AngelList SPV vs Allocations SPV: Best SPV Platform for Fund Managers
AngelList SPV vs Allocations SPV: Best SPV Platform for Fund Managers
Read more
SPVs
Sydecar SPV vs Allocations SPV: What to chose in 2026
Sydecar SPV vs Allocations SPV: What to chose in 2026
Read more
SPVs
Best SPV Platform in the United States (USA) in 2026
Best SPV Platform in the United States (USA) in 2026
Read more
SPVs
Best SPV Platform in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) in 2026
Best SPV Platform in the United Arab Emirates (UAE) in 2026
Read more
SPVs
Carta Pricing vs Allocations Pricing (2026)
Carta Pricing vs Allocations Pricing (2026)
Read more
SPVs
AngelList Pricing vs Allocations Pricing (2026)
AngelList Pricing vs Allocations Pricing (2026)
Read more
SPVs
How to Invest into Real Estate with Allocations: A Beginner's Guide to SPV Funds
How to Invest into Real Estate with Allocations: A Beginner's Guide to SPV Funds
Read more
SPVs
Best Fund Admin & Reporting Tools for VC Investors in 2026: Allocations
Best Fund Admin & Reporting Tools for VC Investors in 2026: Allocations
Read more
SPVs
Convertible Notes: Early Stage Investing with Allocations
Convertible Notes: Early Stage Investing with Allocations
Read more
SPVs
Top 5 Value for Money SPV Platforms
Top 5 Value for Money SPV Platforms
Read more
SPVs
How SPV Pricing Works on Allocations
How SPV Pricing Works on Allocations
Read more
SPVs
Best Fund Admin in 2026: Why Allocations Leads
Best Fund Admin in 2026: Why Allocations Leads
Read more
SPVs
How Allocations Is Changing SPV & Fund Formation
How Allocations Is Changing SPV & Fund Formation
Read more
SPVs
What Makes Allocations the First Choice for Fund Administrators
What Makes Allocations the First Choice for Fund Administrators
Read more
SPVs
Why Choose Allocations for SPVs and Funds in 2026
Why Choose Allocations for SPVs and Funds in 2026
Read more
SPVs
Best SPV Platforms in 2026: Why Allocations
Best SPV Platforms in 2026: Why Allocations
Read more
SPVs
SPV & Fund Pricing in 2026: Allocations
SPV & Fund Pricing in 2026: Allocations
Read more
SPVs
Can I Have Non-U.S. Investors? A Practical Guide for SPVs and Fund Managers
Can I Have Non-U.S. Investors? A Practical Guide for SPVs and Fund Managers
Read more
SPVs
What Do I Need to Do Every Year as a Fund Manager?
What Do I Need to Do Every Year as a Fund Manager?
Read more
SPVs
Do I Need an ERA? A Practical Guide for Fund Managers
Do I Need an ERA? A Practical Guide for Fund Managers
Read more
SPVs
How Much Does It Cost to Create an SPV in 2026?
How Much Does It Cost to Create an SPV in 2026?
Read more
SPVs
Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV): Meaning in Finance, Banking and Real-World Examples
Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV): Meaning in Finance, Banking and Real-World Examples
Read more
SPVs
Top Fund Administration Platforms in 2026
Top Fund Administration Platforms in 2026
Read more
SPVs
Migrate Your Fund to Allocations: A Complete Guide for Fund Managers
Migrate Your Fund to Allocations: A Complete Guide for Fund Managers
Read more
SPVs
What Does “Offshore” Means?
What Does “Offshore” Means?
Read more
SPVs
Comparing 506b vs 506c for Private Fundraising
Comparing 506b vs 506c for Private Fundraising
Read more
SPVs
LLP vs LLC | Choose business structure with Allocations
LLP vs LLC | Choose business structure with Allocations
Read more
SPVs
SPV Meaning in Finance: Complete Guide to Special Purpose Vehicles (2026)
SPV Meaning in Finance: Complete Guide to Special Purpose Vehicles (2026)
Read more
SPVs
The Best AngelList Alternatives in 2026 (Detailed Comparison)
The Best AngelList Alternatives in 2026 (Detailed Comparison)
Read more
SPVs
Understanding Special Purpose Vehicles (SPVs)
Understanding Special Purpose Vehicles (SPVs)
Read more
SPVs
Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV): What It Is and Why Investors Use It
Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV): What It Is and Why Investors Use It
Read more
SPVs
Who Typically Uses SPVs?
Who Typically Uses SPVs?
Read more
SPVs
Understanding SPVs in the Context of Private Equity
Understanding SPVs in the Context of Private Equity
Read more
SPVs
Why Use an SPV for Investment?
Why Use an SPV for Investment?
Read more
SPVs
SPV for Late-Stage and Secondary Investments
SPV for Late-Stage and Secondary Investments
Read more
SPVs
SPV Investment Structures: How Money Flows from Investors to Startups
SPV Investment Structures: How Money Flows from Investors to Startups
Read more
SPVs
SPV Management 101: What Happens After the Deal Closes
SPV Management 101: What Happens After the Deal Closes
Read more
SPVs
SPV in Venture Capital vs Traditional VC Funds: What Investors Need to Know
SPV in Venture Capital vs Traditional VC Funds: What Investors Need to Know
Read more
SPVs
SPV Structures in 2026: How Special Purpose Vehicles Are Evolving in Private Markets
SPV Structures in 2026: How Special Purpose Vehicles Are Evolving in Private Markets
Read more
SPVs
Real Estate SPV: A Complete Guide to Structuring Property Investments with Allocations
Real Estate SPV: A Complete Guide to Structuring Property Investments with Allocations
Read more
SPVs
Best SPV Platform in 2026: Features, Pricing, Compliance & How to Choose
Best SPV Platform in 2026: Features, Pricing, Compliance & How to Choose
Read more
SPVs
Top SPV Platforms in 2026: A Complete Comparison
Top SPV Platforms in 2026: A Complete Comparison
Read more
SPVs
SPV Structure and Governance: Who Controls What?
SPV Structure and Governance: Who Controls What?
Read more
SPVs
SPV Structure Explained: How SPVs Work for Private Investments
SPV Structure Explained: How SPVs Work for Private Investments
Read more
SPVs
Why Special Purpose Vehicles (SPVs) Are Becoming Essential in Modern Investing
Why Special Purpose Vehicles (SPVs) Are Becoming Essential in Modern Investing
Read more
SPVs
Understanding SPV Structures
Understanding SPV Structures
Read more
SPVs
Inside DATCOs: The Rise of Digital Asset Treasury Companies | Allocations
Inside DATCOs: The Rise of Digital Asset Treasury Companies | Allocations
Read more
SPVs
DATCO Stock Performance vs Bitcoin Price: Where to Invest in 2026
DATCO Stock Performance vs Bitcoin Price: Where to Invest in 2026
Read more
SPVs
Private Markets Aren’t Broken, They’re Just Waiting for Better Tools
Private Markets Aren’t Broken, They’re Just Waiting for Better Tools
Read more
SPVs
Digital Asset Treasury Companies: The DATCO Era Begins | Allocations
Digital Asset Treasury Companies: The DATCO Era Begins | Allocations
Read more
SPVs
How Allocations Redefines SPVs, Fund Formation, and Fund Management Software for Today’s Investment Managers
How Allocations Redefines SPVs, Fund Formation, and Fund Management Software for Today’s Investment Managers
Read more
SPVs
How VCs Are Scaling Trust, Not Just Capital
How VCs Are Scaling Trust, Not Just Capital
Read more
SPVs
Digital Asset Treasury Companies (DATCOs) vs Bitcoin ETFs: What’s the Difference?
Digital Asset Treasury Companies (DATCOs) vs Bitcoin ETFs: What’s the Difference?
Read more
SPVs
The 10-Minute Fund: What Instant Fund Formation Really Means
The 10-Minute Fund: What Instant Fund Formation Really Means
Read more
SPVs
Allocation IRR: Measuring Returns in Private Market Deals
Allocation IRR: Measuring Returns in Private Market Deals
Read more
SPVs
How Much Does It Cost to Start an SPV in 2025?
How Much Does It Cost to Start an SPV in 2025?
Read more
SPVs
Allocations Pricing Explained: Transparent, Flat-Fee Fund Administration for SPVs and Funds
Allocations Pricing Explained: Transparent, Flat-Fee Fund Administration for SPVs and Funds
Read more
SPVs
Private Equity SPVs: How Allocations Automates Fund Formation for Modern Investors
Private Equity SPVs: How Allocations Automates Fund Formation for Modern Investors
Read more
SPVs
From Term Sheet to Close: How Automated Deal Execution Platforms Speed Up Venture Investing
From Term Sheet to Close: How Automated Deal Execution Platforms Speed Up Venture Investing
Read more
SPVs
Why Modern Fund Managers Need Better Infrastructure
Why Modern Fund Managers Need Better Infrastructure
Read more
SPVs
AngelList vs Sydecar vs Allocations: The 2025 SPV Platform Showdown
AngelList vs Sydecar vs Allocations: The 2025 SPV Platform Showdown
Read more
SPVs
Fund Setup Software: Building Your First Fund With Allocations
Fund Setup Software: Building Your First Fund With Allocations
Read more
SPVs
Understanding 506(b) Funds: How Private Offerings Stay Compliant
Understanding 506(b) Funds: How Private Offerings Stay Compliant
Read more
SPVs
Allocations: The Complete Guide to Modern Fund Management
Allocations: The Complete Guide to Modern Fund Management
Read more
SPVs
Emerging Managers 101: Why SPVs Are the Easiest Way to Start Raising Capital
Emerging Managers 101: Why SPVs Are the Easiest Way to Start Raising Capital
Read more
SPVs
Asset Allocation Strategies for Modern Portfolios in 2025 ft. Allocations
Asset Allocation Strategies for Modern Portfolios in 2025 ft. Allocations
Read more
SPVs
Deal Allocation Tools: How to Streamline Investor Access to Opportunities
Deal Allocation Tools: How to Streamline Investor Access to Opportunities
Read more
SPVs
SPV Fees Explained: What Sponsors and Investors Should Know
SPV Fees Explained: What Sponsors and Investors Should Know
Read more
SPVs
How to Set Up an SPV: Step-by-Step Guide for Sponsors and Investors
How to Set Up an SPV: Step-by-Step Guide for Sponsors and Investors
Read more
SPVs
Why Delaware for SPVs? Investor Trust, Legal Clarity, Faster Closes
Why Delaware for SPVs? Investor Trust, Legal Clarity, Faster Closes
Read more
SPVs
Best SPV Platform in 2025? Features, Pricing, and How to Choose
Best SPV Platform in 2025? Features, Pricing, and How to Choose
Read more
SPVs
SPV Exit Strategies: What Happens When the Deal Closes
SPV Exit Strategies: What Happens When the Deal Closes
Read more
SPVs
Side Letters in SPVs: What You Need to Know
Side Letters in SPVs: What You Need to Know
Read more
SPVs
SPV K-1 Tax Reporting: What Sponsors and Investors Need to Know (2025 Guide)
SPV K-1 Tax Reporting: What Sponsors and Investors Need to Know (2025 Guide)
Read more
SPVs
What Does an SPV Company Do? (2025 Guide)
What Does an SPV Company Do? (2025 Guide)
Read more
SPVs
Real Estate SPV vs LLC: Which Is Better for Property Investment?
Real Estate SPV vs LLC: Which Is Better for Property Investment?
Read more
SPVs
SPV Tax Reporting: A Complete Guide for Sponsors and Investors
SPV Tax Reporting: A Complete Guide for Sponsors and Investors
Read more
SPVs
The Role of Allocations in Modern Asset Management
The Role of Allocations in Modern Asset Management
Read more
SPVs
Form D & Blue Sky Law Compliance for SPVs: What Sponsors Need to Know
Form D & Blue Sky Law Compliance for SPVs: What Sponsors Need to Know
Read more
SPVs
SPV Company vs Fund: Which Is Right for Your Deal?
SPV Company vs Fund: Which Is Right for Your Deal?
Read more
SPVs
SPV Platform: The Complete 2025 Guide (ft. Allocations)
SPV Platform: The Complete 2025 Guide (ft. Allocations)
Read more
SPVs
How to Choose the Best SPV Platform: A 15-Point Buyer’s Checklist
How to Choose the Best SPV Platform: A 15-Point Buyer’s Checklist
Read more
Fund Manager
What is an SPV? The Definitive Guide to Special Purpose Vehicles
What is an SPV? The Definitive Guide to Special Purpose Vehicles
Read more
Fund Manager
5 best books to read If you’re forging a path in VC
5 best books to read If you’re forging a path in VC
Read more
Investor Spotlight
Investor spotlight: Alex Fisher
Investor spotlight: Alex Fisher
Read more
SPVs
6 unique use cases for SPVs
6 unique use cases for SPVs
Read more
Market Trends
The SPV ecosystem democratizing alternative investments
The SPV ecosystem democratizing alternative investments
Read more
Company
How to write a stellar investor update
How to write a stellar investor update
Read more
Analytics
What’s going on here? 1 in 10 US households now qualify as accredited investors
What’s going on here? 1 in 10 US households now qualify as accredited investors
Read more
Market Trends
SPVs by sector
SPVs by sector
Read more
Market Trends
5 Benefits of a hybrid SPV + fund strategy
5 Benefits of a hybrid SPV + fund strategy
Read more
Products
What is the difference between 506b and 506c funds?
What is the difference between 506b and 506c funds?
Read more
Fund Manager
Why Allocations is the best choice for fast moving fund managers
Why Allocations is the best choice for fast moving fund managers
Read more
Fund Manager
When should fund managers use a fund vs an SPV?
When should fund managers use a fund vs an SPV?
Read more
Fund Manager
10 best practices for first-time fund managers
10 best practices for first-time fund managers
Read more
Analytics
Bitcoin ETFs and 2 other crypto trends to watch in 2022
Bitcoin ETFs and 2 other crypto trends to watch in 2022
Read more
Market Trends
Private market trends: where are fund managers looking in 2022?
Private market trends: where are fund managers looking in 2022?
Read more
Fund Manager
5 female VCs on the rise in 2022
5 female VCs on the rise in 2022
Read more
Analytics
The new competitive edge for VCs and fund managers
The new competitive edge for VCs and fund managers
Read more
Analytics
4 trends in M&A to watch in 2022 (Plus 1 more that might surprise you)
4 trends in M&A to watch in 2022 (Plus 1 more that might surprise you)
Read more
Investor Spotlight
Investor spotlight: Olga Yermolenko
Investor spotlight: Olga Yermolenko
Read more
Analytics
3 stats that show the democratization of VC in 2021
3 stats that show the democratization of VC in 2021
Read more
Allocations secondary market is operated through Allocations Securities, LLC dba AllocationsX, member FINRA/SIPC. To check this firm on BrokerCheck, click on the following link: here. The main FINRA website can be accessed through this link: here. Allocations Securities, LLC is a wholly owned subsidiary of Allocations, Inc.
Copyright © Allocations Inc
Allocations secondary market is operated through Allocations Securities, LLC dba AllocationsX, member FINRA/SIPC. To check this firm on BrokerCheck, click on the following link: here. The main FINRA website can be accessed through this link: here. Allocations Securities, LLC is a wholly owned subsidiary of Allocations, Inc.
Copyright © Allocations Inc
Allocations secondary market is operated through Allocations Securities, LLC dba AllocationsX, member FINRA/SIPC. To check this firm on BrokerCheck, click on the following link: here. The main FINRA website can be accessed through this link: here. Allocations Securities, LLC is a wholly owned subsidiary of Allocations, Inc.
Copyright © Allocations Inc
